Ohms Law

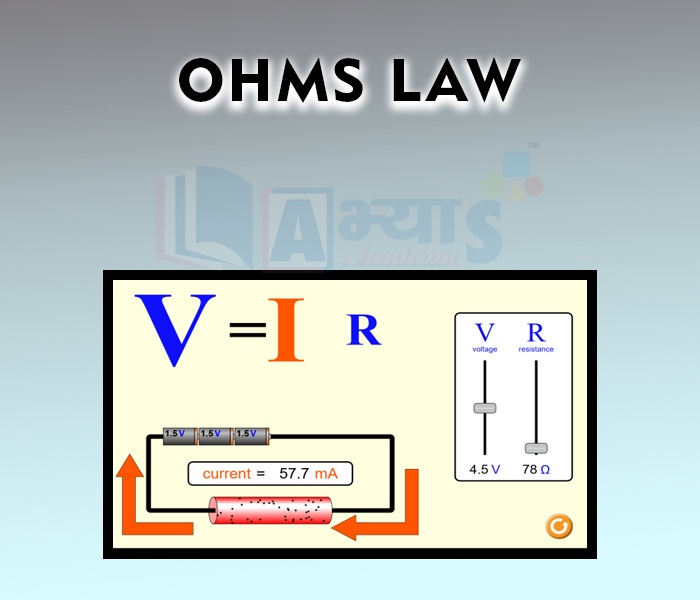
Ohms Law
We all have experienced the situation that when a torch is used for several weeks, its light becomes dim. We say that its cells have become weak.This means that the potential difference has droped to a smaller value because the chemicals have been used up in the chemical reactions. As the potential difference has dropped so less current flows through the bulb, and hence produces less light. So, we can say that the electric current passing through the circuit depends on the potential difference applied across it. The larger is the potential difference, the larger is the current. This relationship between potential difference and current was first discovered by a German physicist Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854) and is stated by the law named after him
Ohm's Law states that the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference between its ends, provided the physical conditions such as temperature of conductor remain unchanged.
He further observed that as we increase the potential the current increases, so we can state that the
i.e., or
where R is a constant which is called resistance of the material.
Unit of resistance
The SI unit of resistance is ohm .
If I = 1 Ampere, V = 1 Volt, then R = 1 .
The resistance of a conductor is 1 ohm if a potential difference of 1 volt is produced across its ends when 1 ampere of the current flows through it.
The conductors, which obey the Ohms law are called the ohmic conductors or linear resistances. All metallic conductors (such as silver, aluminium, copper, iron , etc,) are the Ohmic conductors or linear resistances.
The conductors, which do not obey the Ohms law are called the non-Ohmic conductors or non-linear resistances. Examples are, diode valve, transistors, electrolyte, etc.
Illustration: A 5 V battery is connected to a 10 resistance. Calculate the amount of current flowing through the circuit.
Solution: It is given that
V = 5 V
R = 10
To find I =?
According to Ohm's Law
V = IR
Hence a current of 0.5 A flows through the circuit.
In a circuit n electrons flow through the cross section of a wire in t s when a potential difference V is applied. Write the following steps in sequential order to determine the electric resistance of the wire. (A) Determine the value of electric current , I=ne/t. (B) Note the value of Potential difference V, number of electrons n, time t and the charge e of an electrons. (C) Write the relation, V = IR. (D) The resistance of the wire , R = V/I
| |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation |
How much current will flow through a bulb of resistence | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Two resistors of resistance (A) Use the Ohm's law, V=IR. (B) Determine the effective resistance ( (C) Determine the electric current by using the relation,
| |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.
